Customizing Storage#
By default, LlamaIndex hides away the complexities and let you query your data in under 5 lines of code:
from llama_index.core import VectorStoreIndex, SimpleDirectoryReader
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader("data").load_data()
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(documents)
query_engine = index.as_query_engine()
response = query_engine.query("Summarize the documents.")
Under the hood, LlamaIndex also supports a swappable storage layer that allows you to customize where ingested documents (i.e., Node objects), embedding vectors, and index metadata are stored.
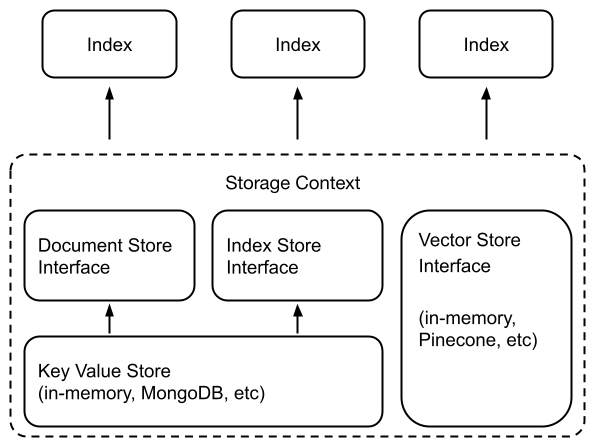
Low-Level API#
To do this, instead of the high-level API,
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(documents)
we use a lower-level API that gives more granular control:
from llama_index.core.storage.docstore import SimpleDocumentStore
from llama_index.core.storage.index_store import SimpleIndexStore
from llama_index.core.vector_stores import SimpleVectorStore
from llama_index.core.node_parser import SentenceSplitter
# create parser and parse document into nodes
parser = SentenceSplitter()
nodes = parser.get_nodes_from_documents(documents)
# create storage context using default stores
storage_context = StorageContext.from_defaults(
docstore=SimpleDocumentStore(),
vector_store=SimpleVectorStore(),
index_store=SimpleIndexStore(),
)
# create (or load) docstore and add nodes
storage_context.docstore.add_documents(nodes)
# build index
index = VectorStoreIndex(nodes, storage_context=storage_context)
# save index
index.storage_context.persist(persist_dir="<persist_dir>")
# can also set index_id to save multiple indexes to the same folder
index.set_index_id("<index_id>")
index.storage_context.persist(persist_dir="<persist_dir>")
# to load index later, make sure you setup the storage context
# this will loaded the persisted stores from persist_dir
storage_context = StorageContext.from_defaults(persist_dir="<persist_dir>")
# then load the index object
from llama_index.core import load_index_from_storage
loaded_index = load_index_from_storage(storage_context)
# if loading an index from a persist_dir containing multiple indexes
loaded_index = load_index_from_storage(storage_context, index_id="<index_id>")
# if loading multiple indexes from a persist dir
loaded_indicies = load_index_from_storage(
storage_context, index_ids=["<index_id>", ...]
)
You can customize the underlying storage with a one-line change to instantiate different document stores, index stores, and vector stores. See Document Stores, Vector Stores, Index Stores guides for more details.
Vector Store Integrations and Storage#
Most of our vector store integrations store the entire index (vectors + text) in the vector store itself. This comes with the major benefit of not having to explicitly persist the index as shown above, since the vector store is already hosted and persisting the data in our index.
The vector stores that support this practice are:
- AzureAISearchVectorStore
- ChatGPTRetrievalPluginClient
- CassandraVectorStore
- ChromaVectorStore
- EpsillaVectorStore
- DocArrayHnswVectorStore
- DocArrayInMemoryVectorStore
- JaguarVectorStore
- LanceDBVectorStore
- MetalVectorStore
- MilvusVectorStore
- MyScaleVectorStore
- OpensearchVectorStore
- PineconeVectorStore
- QdrantVectorStore
- RedisVectorStore
- UpstashVectorStore
- WeaviateVectorStore
A small example using Pinecone is below:
import pinecone
from llama_index.core import VectorStoreIndex, SimpleDirectoryReader
from llama_index.vector_stores.pinecone import PineconeVectorStore
# Creating a Pinecone index
api_key = "api_key"
pinecone.init(api_key=api_key, environment="us-west1-gcp")
pinecone.create_index(
"quickstart", dimension=1536, metric="euclidean", pod_type="p1"
)
index = pinecone.Index("quickstart")
# construct vector store
vector_store = PineconeVectorStore(pinecone_index=index)
# create storage context
storage_context = StorageContext.from_defaults(vector_store=vector_store)
# load documents
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader("./data").load_data()
# create index, which will insert documents/vectors to pinecone
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(
documents, storage_context=storage_context
)
If you have an existing vector store with data already loaded in,
you can connect to it and directly create a VectorStoreIndex as follows:
index = pinecone.Index("quickstart")
vector_store = PineconeVectorStore(pinecone_index=index)
loaded_index = VectorStoreIndex.from_vector_store(vector_store=vector_store)